 MENU
MENUX
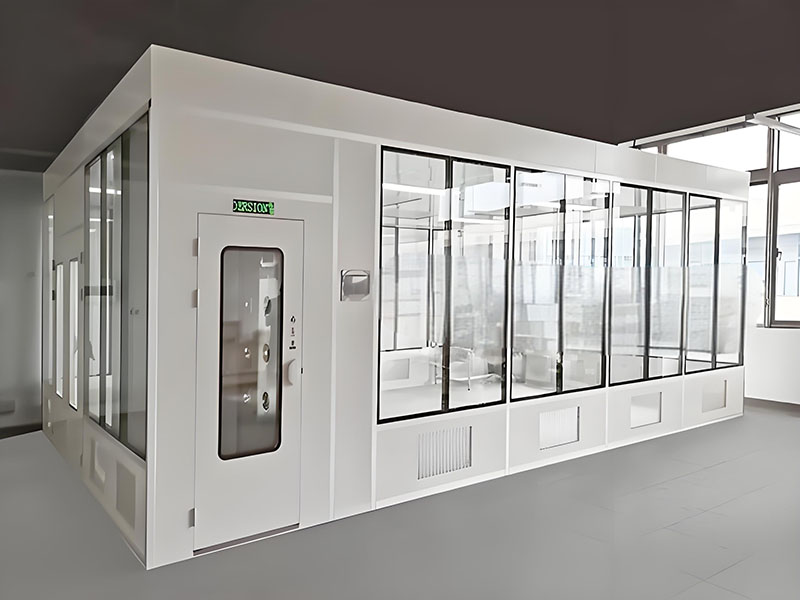
Class 5 Modular Cleanrooms are a type of controlled environment that adheres to stringent cleanliness standards established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Specifically, Class 5 cleanrooms fall under ISO 14644-1’s classification system, which categorizes cleanrooms based on the maximum allowable levels of airborne particulate contamination.
Applications of Class 5 Modular Cleanrooms:
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Essential for producing microchips and other electronic components where even minute levels of contamination can lead to defects.
Pharmaceutical Production: Used in the manufacturing of sterile products and in laboratories where sensitive processes occur.
Biotechnology Research: Important for research and development activities that require a clean environment to prevent contamination of samples.
Medical Device Manufacturing: Ensures that devices are produced in a sterile environment, complying with health regulations.
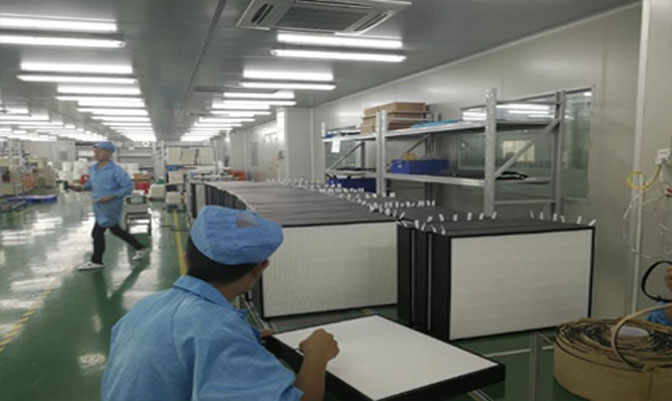
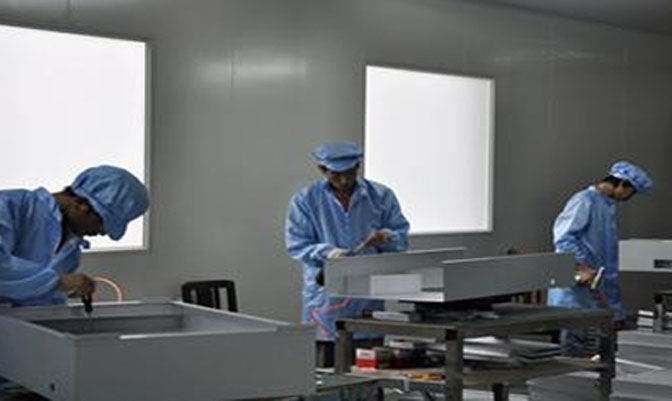










ISO class 5 modular cleanrooms allow a maximum of 3,520 particles (≥0.5 µm) per cubic meter, ensuring a highly sterile environment.
Commonly used in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and semiconductor manufacturing for critical processes requiring low contamination.
Typically built with modular panels, HEPA filters, and specialized HVAC systems to maintain cleanliness.

Pharmaceuticals: Essential for drug production and packaging to prevent contamination.
Biotechnology: Used in labs and manufacturing to ensure product integrity during critical research processes.
Semiconductors: Necessary for the fabrication of microchips where even minor contamination can lead to defects.
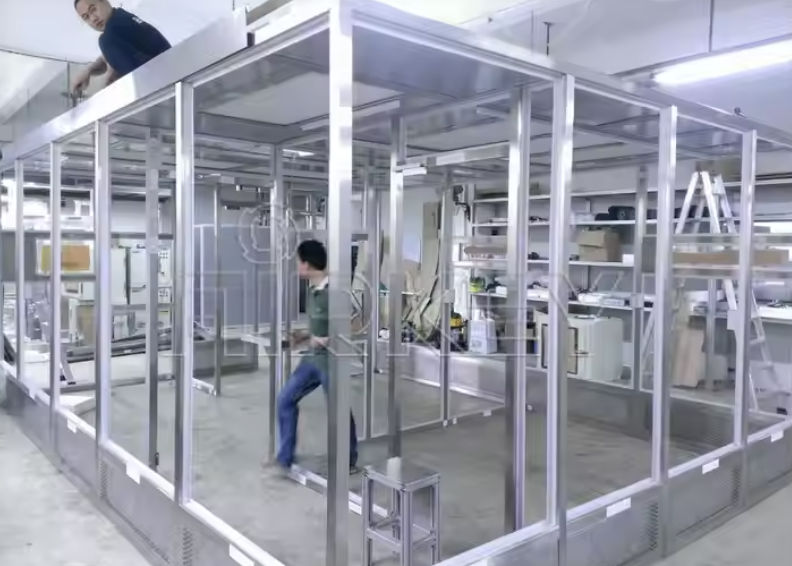
Modular Design
Constructed using pre-fabricated panels for flexibility and easy installation.
Airflow Management
Designed with laminar airflow systems to minimize contamination risks and maintain particle levels.
Custom Features
Can include airlocks, pass-throughs, and specialized equipment tailored to specific operational needs.

1.HEPA Filtration: Must use HEPA filters to ensure the removal of particulate contaminants from the air.
2.Monitoring: Regular monitoring of airborne particles is crucial to maintain ISO compliance.
3.Ventilation Rate: Requires specific air changes per hour (ACH) to ensure adequate air quality.

Cost-Effective:
Generally less expensive than traditional cleanroom construction, reducing overall investment.
Flexibility:
Easily expandable or reconfigurable to adapt to changing operational needs.
Quick Installation:
Modular components allow for faster setup, minimizing downtime during construction.
Regular Cleaning: Scheduled cleaning protocols and disinfection are essential to prevent contamination buildup.
Equipment Maintenance: Routine checks and maintenance of HVAC and filtration systems to ensure proper function.
Staff Training: Continuous training for personnel on contamination control procedures is vital for compliance.

Controlled Environment: Requires specific temperature and humidity levels tailored to the applications being performed.
Monitoring Systems: Uses sensors and control systems to ensure environmental parameters are consistently maintained.
Application Specific: Different processes may have unique requirements for optimal conditions.

1.Vary depending on size, materials, and design complexity.
2.Include utilities, maintenance, and staff training, impacting the overall budget.
3.Well-maintained cleanrooms can lead to higher product quality and reduced defects.
Contamination Control: Staff must understand contamination sources and how to mitigate them effectively.
Cleanroom Protocols: Training on proper gowning, cleaning procedures, and equipment use is essential.
Emergency Procedures: Staff should be familiar with emergency protocols and response plans to ensure safety.

1.Initial Validation:
Involves testing air quality, particle counts, and environmental controls to meet ISO standards.
2.Ongoing Monitoring:
Regular testing and monitoring are necessary to ensure continued compliance.
3.Documentation:
Keeping detailed records of testing results and maintenance activities is crucial for regulatory compliance.