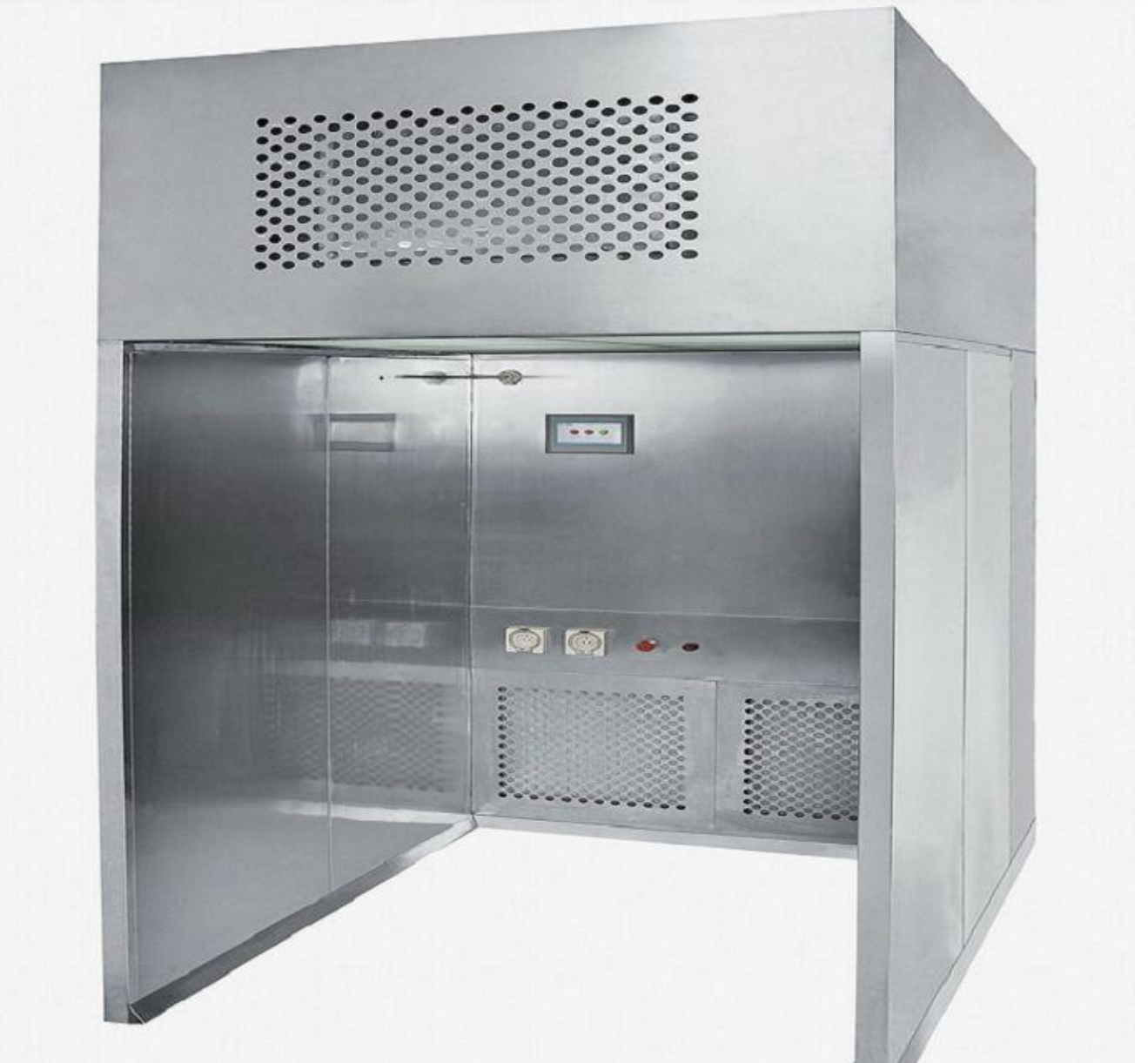
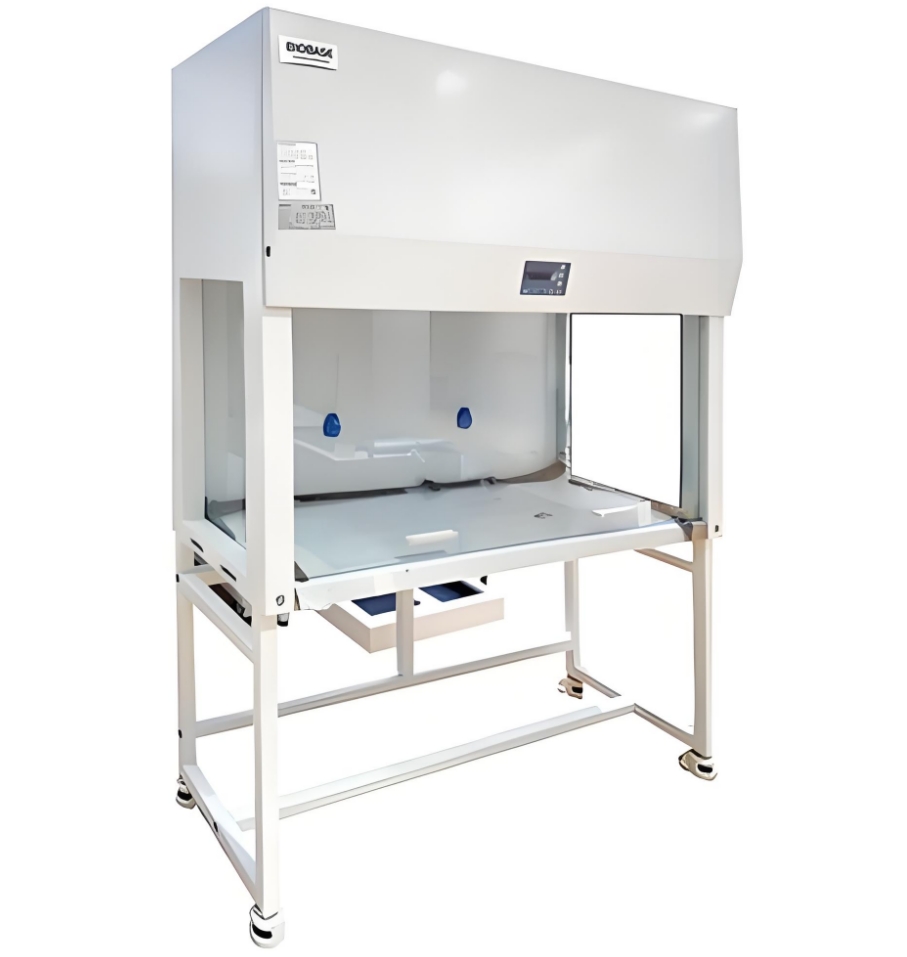
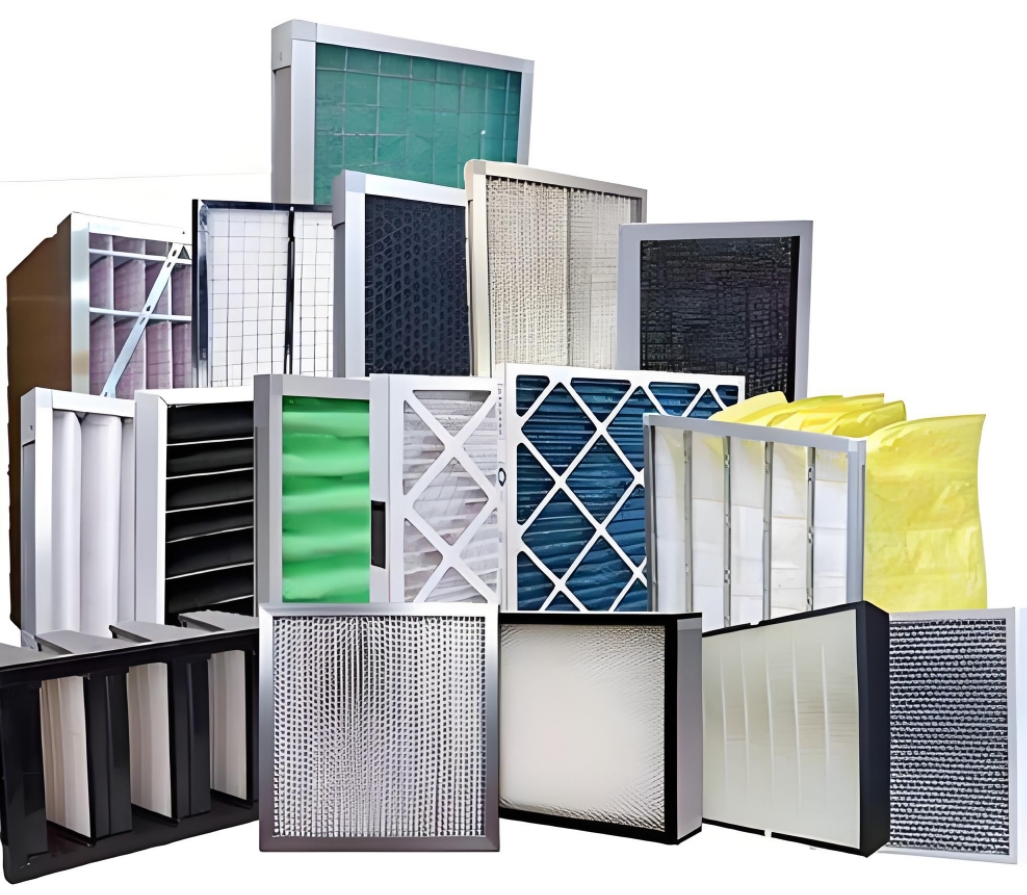
Ensuring the success rate of stem cell transplantation in a Clean bench environment involves several key practices to maintain sterility, minimize contamination, and optimize cell viability
Use of HEPA Filters
Clean benches should be equipped with HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters to create an ultra-clean, sterile environment by removing airborne particles and pathogens, crucial for stem cell handling.
Sterile Techniques
Sterile techniques are critical in laboratory settings, particularly when handling sensitive materials such as stem cells or tissue cultures. Maintaining sterility helps prevent contamination, which could compromise the integrity of experiments or affect the health of test subjects. One of the key practices in sterile techniques is ensuring that all equipment, tools, and materials are sterilized before use.
Key Steps in Sterilization:
l Sterilize all equipment: Instruments such as pipettes, tweezers, and culture flasks should be autoclaved or sterilized using appropriate methods before being introduced into the clean workspace.
l Sterilize tools and surfaces: Wipe down all surfaces of the clean bench and laboratory tools with disinfectants to eliminate any potential microbial threats.
l Sterilize consumables: Reagents, culture media, and other materials should be filtered, autoclaved, or irradiated to ensure they are free of contaminants.
In addition to sterilization, researchers must adhere to strict aseptic techniques. These techniques help maintain a sterile environment by preventing direct contact with non-sterile surfaces and minimizing exposure to airborne contaminants. Simple yet essential practices include washing hands, wearing appropriate protective gear, and working in a laminar flow hood to maintain air quality.
Controlled Environment
Regular monitoring of the temperature, humidity, and airflow within the clean bench is essential to maintain the ideal conditions for stem cell survival and function.
Proper Handling of Stem Cells
Proper handling of stem cells is vital to preserve their viability and functionality. Stem cells are sensitive to environmental conditions like temperature, pH, and contamination, so it’s essential to minimize exposure to air and light. Maintaining a sterile environment is key to prevent oxidative stress or microbial contamination, which could compromise the cell culture and subsequent experiments.
When handling stem cells, it’s crucial to maintain optimal culture conditions. This includes controlling temperature (typically 37°C), CO2 levels (around 5%), and humidity. Regular monitoring of these factors ensures that stem cells have the best possible environment for growth and differentiation. Additionally, sterile reagents and media are essential to avoid .
introducing contaminants into the culture.
The physical manipulation of stem cells should also be done carefully to minimize damage. Over-handling or excessive use of enzymatic treatments (like trypsin for dissociation) can affect the stem cells' health and function. Using sterile, calibrated instruments and minimizing mechanical stress will help maintain the stem cells' integrity, ensuring successful transplantation or other downstream applications.
Regular Cleaning and Disinfection
The clean bench and all surfaces in the workspace should be cleaned and disinfected regularly using appropriate sterilizing agents to maintain a contaminant-free environment.
By combining these practices, researchers can significantly improve the success rate of stem cell transplantation and ensure the reliability of their experimental results.
 18186671616
18186671616 pengwu1616@gmai.com
pengwu1616@gmai.com
 MENU
MENU














